Archibald Maclaren was an instructor of physical
education and fencing. In 1864 he produced a manual on fencing for military
instructors. In 1868 it was combine with his Military System of Gymnastic
Exercises, with some updates. The 1868 edition was printed in London under the
superintendence of Her Majesty’s Stationery Office. The General Order for Horse
Guards stated:
“The Field Marshal Commanding-in-Chief has directed
the following Regulations for the Gymnastic and Fencing Instruction, and for
the Club Exercise, to be printed and bound together in one volume, as more
convenient for reference and use than the three separate books hitherto
published. By Command, Wm. PAULET, A.G.”
He produced the instructional manual during a
period where there was concern that the British military physical fitness was
not up to standard. The British Army was keen to open schools of physical
training as a result of the Crimean War, where, as Major Frederick Hammersley
said “the general health and fitness of recruits and soldiers left a good deal
to be desired.”
The first part of the manual, comprising a large
portion, is dedicated to the gymnastic exercises. It includes a variety of
exercises covering such activities as dumb bells, bar bells, vaulting horse,
rings, free climbing and escalading (the surmounting of a wall or other
obstacle too elevated to be surmounted by a leap or a vault). Maclaren says of
the exercises that “Every exercise comprised in the present system has been
selected for its value in one of two aspects: the first, or elementary aspect,
being the manner and degree in which it tends to cultivate the physical
resources of the body by increasing its dexterity and rapidity of action, its
strength in overcoming resistance, and its power of enduring protracted
fatigue; while the second, or practical aspect, is the manner and degree in
which its practice may be brought to aid directly in the professional duties of
the soldier”.
A System of Fencing
Maclaren’s system should be noted for its attempt
at efficiency (4 parries, rather than 8), while also giving an in depth
analysis of how and why the actions are to be made. He studied fencing in
France, presumably the source for most of his material. As it is a system for
the military, the lessons are presented for instructors to use in individual or
group lessons. The manual is laid out with an introduction and explanation for
each action, followed by instructions on how to teach the action.
Maclaren begins by defining fencing, and indicates
that the foil is taught because he considers the thrust to be the most
effective way of disabling an opponent. The movements of fencing can be
arranged under four heads:
-Preliminary Movements or Positions
-Defensive Movements or Parries
-Offensive Movements or Attacks
-Return Attacks
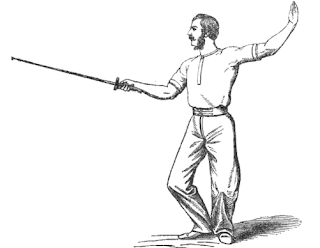
PART I - Preliminary Movements
and Positions
This details the movements to come on guard,
starting from a position of attention and finishing in the guard.
He emphasizes that “Too much care cannot be
bestowed upon the acquisition of a correct guard, for on this depends
much of the force and accuracy of the movements in attack
and defence.”
He notes that the power of the lunge comes from
straightening of the left leg, and that the left hand should fall in position
to within a few inches of the thigh. Maclaren concludes that the concentrated
action of all the different parts of the body renders the
sword-thrust so deadly.
 |
| Coming On Guard |
It is interesting to note that his instructions for
the “longe” (lunge) were altered from his original 1864 publication. In the
1864 publication of a “System of Fencing” he instructs that in the lunge “The
column of the body is not now, as in the guard, held perpendicular to
the centre of the span of the lower limbs; it has
partaken of their forward action, and by its fall has added to their
momentum”.
By 1868 he has changed this to keeping the upright
position, which was common in the French method. This may have occurred
following criticism from other sources, including Richard Burton (Burton notes
in his “Sword Exercise”: Mr. MacLaren, in his ' System of
Fencing,' &c. sensibly advocates "resting the
weight of the body equally upon both legs." He also lowers the
right hand in the Lunge, and he throws the trunk forward, perhaps
with a little exaggeration. Other than this criticism, though, Burton was an
ardent supporter of Maclaren and preferred his gym to that of Angelo’s.)
 |
| On the Word "Thrust" |
 |
| The Longe |
Finally with the guard, the advance and retreat,
the lunge and the recover, the “learner must be taught to execute them with
faultless precision and accuracy before any attempt is made to carry him into
the other divisions of the art.”
PART II - Defensive Movements or Parries
Maclaren explains his teaching method for a group.
It is to single out one man to teach, and then repeat with each individual as
the others circle around to observe.
He gives an explanation of the lines. There are the
inner and outer lines, and the upper and under lines. These create four openings.
The parry is the special protection for each of the four openings. The
defensive motions are made from the engagement. These two movements are called
respectively the inner and outer engagements, or the
engagements of quarte and tierce. The hand stays in the central
position when pressing from the inside, and the hand turns when pressing from
the outside.
Maclaren notes that in the quarte parry the hand
need only pass a few inches to the inner line to make the defense, for as the
attack “passed farther and farther outwards; and, although at the
moment of its contact with the defending blade, it may have been made
to deviate from the true line but a small fraction of an inch, yet
when the longe is completed it will have passed a foot outside the most outlying
portion of the breast; just as a shot quitting the
muzzle of a gun, and deviating a hair's breadth from the straight
line, will be many yards from it at the end of its flight, and the
longer its flight the wider its deviation.”
 |
| Parry of Quarte |
 |
| Parry of Tierce |
He adds that there is a second defense for each
line, that being the parries of Quinte, Sixte, Octave, and Prime. The object of
the second defense was to give variety in the defenses, but since the same
attack deceives both parries, it requires a double labor to learn. He also
notes (as Angelo says) that prime is a broadsword, not a smallsword parry.
Counter parries are protection against disengages.
His explanation offers an example of Maclaren’s detailed description:
“The instructor and learner are again in the
position of adversaries, with the blades joined on the inner line.
The instructor, extending his arm, advances his point above the learner's hand.
We have seen that quarte will guard this. But were the instructor to lower his
point during the extension, and thrust on the under division; or to pass a
little farther and thrust on the under line outside; or go still farther, and,
elevating the point, thrust above the hand outside, what then? As the attacking
blade sinks from the upper to the under line, eluding the
contact of the defending one as it completed its parry (quarte), the
latter has but to sweep on, while the arm remains stationary forming a central
point or pivot on which the hand and foil revolve, and, whether the assailing
blade terminate its attack on one of the under lines, or rise above
the hand on the outer line, the defending blade, if revolving with sufficient
rapidity, must overtake it; and as it comes up to the point from which it
started, completing its circle, will pass it off as if by its first and simple
parry.' This is called a Counter Parry, and there are
four of this description, corresponding to and receiving their names
from, the simple parries.”
PART III - Offensive Movements or Attacks.
Maclaren defines the target as limited to between
the waist and the collarbone, and extending from armpit to breastbone. On
special occasions it might be further reduced to a circle of a few
inches in diameter, marked on the center of this space, for the
practice of accuracy. He suggests the use of this target because, besides
developing accuracy, it is most likely to deliver a killing blow.
He divides attacks in to three Orders (Direct, Indirect,
and Counter Attacks), which are then subdivided in to Series. After each Series
are instructions on teaching the action.
For the First Order of Direct attacks, the First
Series is made Under the Blade, and should be made with opposition. As the
covering of one line in a defensive position exposes another, a disengagement
is required. Two consecutive disengagements is called the One Two. Three
separate consecutive disengagements is called the One Two Three, but is a
method falling in to disuse for its complexity.
The Second Series of instruction goes around the
blade, the Double to deceive the counter parry. Another example of the detail
Maclaren goes in to describe the action:
“Again instructor and learner stand in
front of each other, the blades joined on the inner line. The learner
makes the disengagement to the outer line which the instructor parries with
counter quarte. This formation of counter quarte on the disengagement
to the outer line leaves the blades respectively in the same position as before
the attack was made; but if, during the act of forming the counter quarte,
the attacking blade keeps the lead, and as the revolving blade on the defence
comes up on the outer line on its counter, neutralizing the first
disengagement, the attacking blade passes to the inner line, again dips and
again rises to the outer line, the original opening will be found. Thus
the second movement is actually a circle formed within the larger
circular defence, starting from and terminating at the opening outside above
the hand…As in the One Two Three and the Counter Counter, The more
complicated of these combinations are seldom made in the assault; but
in the lesson they may be accurately made, and should be assiduously practiced.”
The Third Series is over the blade. This is the cut
over. In addition you can make the cut over with the semi-double, and other attacks
may follow the cut over, such as the one two and the double.
Maclaren notes that the cut over is more effective
as a second attack than as a first. It is more easily and safely made when the
adversary's point is elevated than when it is level; or when his arm is much
drawn back.
Maclaren states that “combined attacks
in fencing are, on a small scale facsimiles of the
approaches made by a besieging force,—a series of zig-zags, getting
nearer and nearer at each move to the point assailed until the intervening
distance can be cleared in a final spring.”
The Second Order consists of Indirect Attacks. They
are made previous to a movement of menace or assault, to distract the
adversary’s attention, to disturb the security of his position, or to mislead
his judgement.
The First Series is the Changement. The Second Series
is the Double Engagement. The Third Series is the Beat, which drives the
opposing blade a sufficient distance to enable a thrust to reach the breast. The
Fourth Series is the beat reverse, an indirect attack that combines the
advantages of both changement and beat. The Fifth Series is the Absence,
relying on a sense of touch and anticipating a beat with the blades quit.
The sixth series is the Pressure, which consists of a
slight addition to the engagement, by bringing the point lower down on the
forte of the opposing blade; and although at the
disadvantage of foible to forte, pressing it out of the
line, until the opening desired be obtained.
The Third Order is Counter Attacks. Maclaren
describes these as an alternative to a defensive movement against an indirect
attack.
The First series is the Changement, which is a
movement called the Counter Disengagement. The Second Series is on the
Double Engagement. The same counter attacks may be made on the double
engagement. The Third Series is on the Beat, and the same counter attacks
may be made on the beat. If the counter attacker perceives the preparation of
the beat attack, they can advance their point with opposition, and the beat
will arrive too late or be delivered on the forte of the advancing blade and
therefore be insufficient. The Fourth Series is on the Beat Reverse, which
can be done on the counter disengagement. The Fifth Series is on the
Absence and the Sixth Series is on the Pressure.
PART IV. Return Attacks (the
Riposte).
Maclaren states that no parry should ever be formed
without its being followed up by a return. He also notes that the parry is
actually aided by the fullness of the attacker’s lunge, bringing the assailants
breast close to the point of the opposing blade. The defender can lunge on the
return if the adversary feels the attack parried and recovers, so Maclaren
recommends that both the return with a simple extension and return with the
lunge should be practiced. The returns are named after the parries from which
they are made. Thus the return after the parry of quarte is called
the Return in quarte; and that after the parry of tierce, the Return
in tierce, &c., &c.
After the First Series of simple returns, the Second
Series is the Returns Reverse to the outside line. The Third Series is Second
Returns, the Fourth Series is the Double Return, the Fifth Series is Double
Return Reverse, the
Sixth Series is The Return Cut-Over (This is most
effective when the adversary is on the recovery of the lunge.)
Another form of Second Attack can be made from the
lunge, if the adversary is careless in his return, or makes it too complicated,
the attacker can remain in the lunge and parry the return, giving a second
return. Maclaren notes that there is danger of exposure in lingering in the lunge,
but a smart fencer can use it to bait a trap. Maclaren provides lesson in this
with the straight thrust, the disengagement and the cut over.
Indirect Return Attacks are coupled with second
actions, such as the beat, the graze, bindings. So for instance the defender
would make a firm parry in quarte, then give a firm beat and deliver the
thrust.
Irregular Attacks
These are a series of return offensive
movements called time attacks, which are made during the adversary’s
attack, and not at its conclusion. These differ from counter attacks, inasmuch
as they are made on direct and not on indirect attacks of an
adversary. They can be practiced with an opponent advancing within distance, or
withdrawing their hand during the attack.
The Assault
Maclaren gives rules for the Assault. Initially the
Assault should be conducted under the supervision of the instructor, and limited
to selected movements. He notes that when fencing against different adversaries
“No two men fence absolutely alike; and movements that are found effective
against one adversary prove quite ineffective against others. All that an
instructor therefore should aim at is to teach the learner the nature and
purpose of the several movements as set down in his book of
instructions, and to qualify him to execute them with perfect precision and the
greatest possible quickness…the instructor can give him the hand, so
to speak, of the swordsman, the head he must provide for
himself.”
A few general rules for conducting the assault are
here added.
1. All exposed parts of the body to be
thoroughly protected. The head and face by a strong, hand-wrought wire mask.
The neck and breast by a stout leather jacket reaching from the chin to a few
inches below the waist, with a well-fitting collar buttoning (behind) around
the neck. The lower part of the body by a leather flap or apron,
either attached to the jacket or buckled round the waist. The right hand by a
soft and pliable leather glove or gauntlet, well padded on the back.
2. The adversaries to fall on guard beyond hitting
distance.
3. .When both adversaries longe at the
same time, and both hits are on the targets, to count for neither; if only one
hit be on the target, such hit to count.
4. When both adversaries thrust at the
same time, but one only with the longe, and both hits are on the target, to
count for the hit given on the longe.
5. It is perfectly fair to make a second attack on
the same longe, but if at the time of the second attack the adversary
gives a return thrust, and both hits are on the target, the return only to
count.
The Salute
Maclaren then describes the Salute in Quarte and
Tierce. It is “Performed on occasions or special encounters, or ‘Assaults of Arms’,
as they are called, for the double purpose of suppling and preparing
the fencer for the assault, and of showing in a graceful and
advantageous manner to spectators the chief movements and
positions of the art.”
The remainder of the fencing manual gives a listing
of the class lessons. This is followed by a short exercise for a bayonet
engaged with a bayonet. This is followed, for the last section, with a series
of exercises for the regulation clubs, applicable to all stations where dumb
and bar bells are not supplied.















No comments:
Post a Comment